Start Building
Key concepts
- All endpoints return either a JSON object or an array.
- Data is returned in ascending (oldest first, newest last) order, if not stated otherwise.
- You might use the ?order=desc query parameter (when available) to reverse this order.
- By default, we return 100 results at a time. You have to use ?page=2 to list through the results.
- All time and timestamp related fields (except server_time) are in seconds of UNIX time.
- All amounts are returned in Lovelaces, where 1 ADA = 1 000 000 Lovelaces.
- Addresses, accounts and pool IDs are in Bech32 format.
- All values are case sensitive.
- All hex encoded values are lower case.
- Examples are not based on real data. Any resemblance to actual events is purely coincidental.
- We allow to upload files up to 100MB of size to IPFS. This might increase in the future.
- We allow maximum of 100 queued pins per IPFS user.
Keep in mind we use pagination (100 items per default) and that it starts from page 1, unlike traditional indexing.
Available networks
The default Blockfrost network is Cardano mainnet, but we also support Cardano testnets (preview and preprod) and IPFS networks.
| Name | API Endpoint (network + version) |
|---|---|
| Cardano mainnet | https://cardano-mainnet.blockfrost.io/api/v0/ |
| Cardano preprod | https://cardano-preprod.blockfrost.io/api/v0/ |
| Cardano preview | https://cardano-preview.blockfrost.io/api/v0/ |
| IPFS | https://ipfs.blockfrost.io/api/v0/ |
The schema of full API endpoint path is a composition of the specific network, appended by the API version and the call itself.
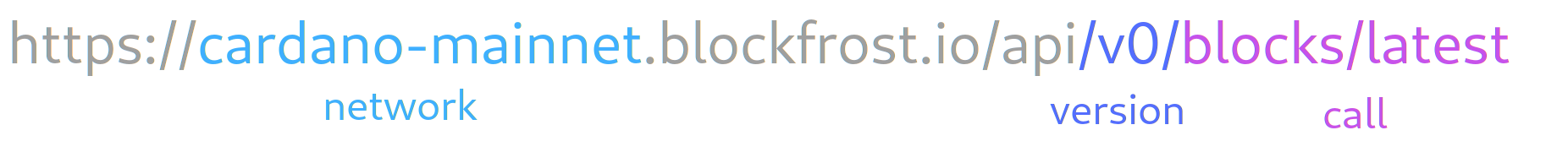
Each network has its own token. Using token created for another network will result in Error 403 with message "Network token mismatch".
Limits
There are three types of limits we are enforcing:
The first depends on your plan and is the number of request we allow per day. We defined the day from midnight to midnight of UTC time.
The second is rate limiting. We limit an end user, distinguished by IP address, to 10 requests per second. On top of that, we allow each user to send burst of 500 requests, which cools off at rate of 10 requests per second. In essence, a user is allowed to make another whole burst after (currently) 500/10 = 50 seconds. E.g. if a user attempts to make a call 3 seconds after whole burst, 30 requests will be processed. We believe this should be sufficient for most of the use cases. If it is not and you have a specific use case, please get in touch with us, and we will make sure to take it into account as much as we can.
The third is applicable to IPFS only. There is a maximum of allowed queued items scheduled to be pinned. Once an item becomes pinned (changes state from queued to pinned), you can call the pin operation again, adding additional item(s) to the queue.
If you'd like to use higher limits or whitelist IPs, please upgrade to Enterprise plan by contacting our support.
Errors
The following are HTTP status code your application might receive when reaching Blockfrost endpoints and it should handle all of these cases.
- HTTP 400 return code is used when the request is not valid.
- HTTP 402 return code is used when the projects exceed their daily request limit.
- HTTP 403 return code is used when the request is not authenticated.
- HTTP 404 return code is used when the resource doesn't exist.
- HTTP 418 return code is used when the user has been auto-banned for flooding too much after previously receiving error code 402 or 429.
- HTTP 425 return code
- In Cardano networks, it is used when the user has submitted a transaction when the mempool is already full, not accepting new txs straight away.
- In IPFS network, it is used when a user has reached the maximum allowed items queued to be pinned.
- HTTP 429 return code is used when the user has sent too many requests in a given amount of time and therefore has been rate-limited.
- HTTP 500 return code is used when our endpoints are having a problem.
Handling common errors
Receiving 400:
- Inspect the error message, usually, it says what the error is and how to resolve it
- Malformed input: check if you use Bech32 and if you're not querying items from different network (e.g. querying testnet address
addr1_test...on Cardano Mainnet)
Receiving 402:
- If using IPFS, check if your quota hasn't been exceeded. Then either remove some pins or upgrade your plan
- Consider upgrading plan
- Check if your
project_idhasn't leaked: see WARNING - Consider implementing cache
Receiving 403:
- Missing, invalid, badly copied or deleted
project_id - Network mismatch: see CAUTION
Receiving 404:
- The resource doesn't exist on the blockchain (yet), visit our Cardano support page for a more detailed explanation
Receiving 425 (Cardano):
- The network is most likely under huge load or an intermittent network error has ocurred. Please retry submitting the transaction and in case you receive another 425, wait a few seconds before trying again.
Receiving 425 (IPFS):
- You have reached the limit of your pin queue. IFPS cluster might be under load or you might be pinning too many (or large) items and your pins are waiting in the pin queue. Please wait a few moments before trying again. We recommend checking for the
stateof the pins by querying/ipfs/pin/list. Once thestatechangesqueued->pinned, you can add a new item to the pin queue.
Receiving 429:
- Consider upgrading plan to
ENTERPRISE, which allows Custom rate-limiting rules - Consider implementing cache
Receiving 5xx:
- Wait a few moments before retrying again and if the problem still persists, please contact our support and share the call details (URL) with us. We constantly monitor all backends for 5xx errors, but we're also grateful for your reports.